Exosomes Derived From Schwann Cells Alleviate Mitochondrial Dysfunction & Necroptosis After Spinal Cord Injury
In a recent study published in the Free Radical Biology and Medicine Journal (Elsevier), Xu et al. have discovered a promising avenue for mitigating the devastating consequences of spinal cord injury (SCI).
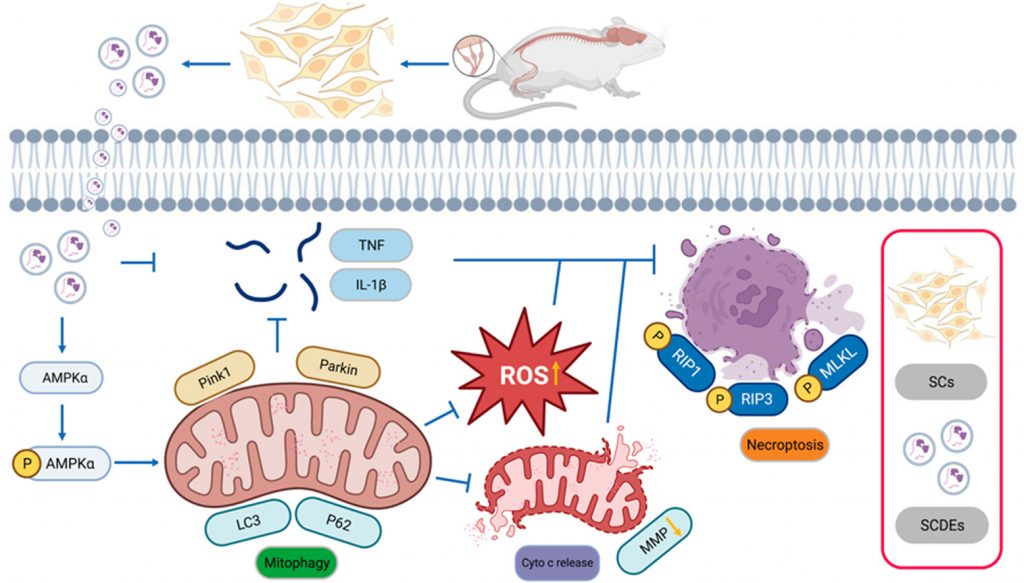
Despite SCI being a major cause of disability, viable therapeutic options are limited. Understanding the intricate pathways leading to mitochondrial dysfunction has become crucial for identifying effective targets to alleviate the repercussions of SCI. The study aimed to assess the efficacy of exosomes derived from Schwann cells (SCDEs) in safeguarding against mitochondrial dysfunction.
The research utilized a rat model of compressed SCI and in vitro experiments with rat pheochromocytoma cells (PC12) subjected to oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD).
The following key findings were reported:
-
Mitigation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: SCDEs demonstrated effectiveness in mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation following SCI, concurrently reducing necroptosis—a process associated with programmed cell death.
-
Enhanced Mitophagy in PC12 Cells: In vitro experiments on PC12 cells revealed that SCDEs enhanced mitophagy, leading to a reduction in reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory cytokines triggered by OGD-induced injury. This mitigation effect extended to improved mitochondrial function and reduced necroptosis.
-
AMPK Signaling Pathway Activation: Mechanistically, SCDEs were found to induce cellular mitophagy through the activation of the AMPK signaling pathway—an essential pathway involved in cellular energy regulation.
In summary, the study strongly suggests that SCDEs hold significant promise as a therapeutic approach for managing SCI. By elucidating the role of AMPK-mediated mitophagy in reducing cell damage, this research opens novel prospects for enhancing neuro-pathological outcomes following SCI.
This breakthrough not only contributes to our understanding of SCI but also paves the way for the development of innovative therapeutic strategies harnessing the potential of Schwann cell-derived exosomes. As the field progresses, these findings may bring us closer to more effective treatments for spinal cord injuries and improved outcomes for individuals affected by this challenging condition.
Image Credits: Xu et al. Free Radical Biology and Medicine (2023)