Innovative Approach to Stroke Recovery: Extracellular Vesicles in Focus
Dr. Devika S Manickam, active member of our scientific board, will present her latest findings at the Targeting Extracellular Vesicles 2024 Congress this October. Her research focuses on the delivery of mitochondria-containing extracellular vesicles (EVs) to the blood-brain barrier.
Recently shared as a pre-print, ongoing research led by Dr. Manickam explores the potential of EVs containing mitochondria to address ischemic stroke-induced neurological dysfunction.
Ischemic stroke often causes mitochondrial dysfunction in brain endothelial cells (BECs), crucial components of the blood-brain barrier. In a previous pilot study, Dr. Manickam’s team demonstrated the efficacy of intravenously administered human BEC (hBEC)-derived mitochondria-containing EVs in a mouse model of stroke induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo).
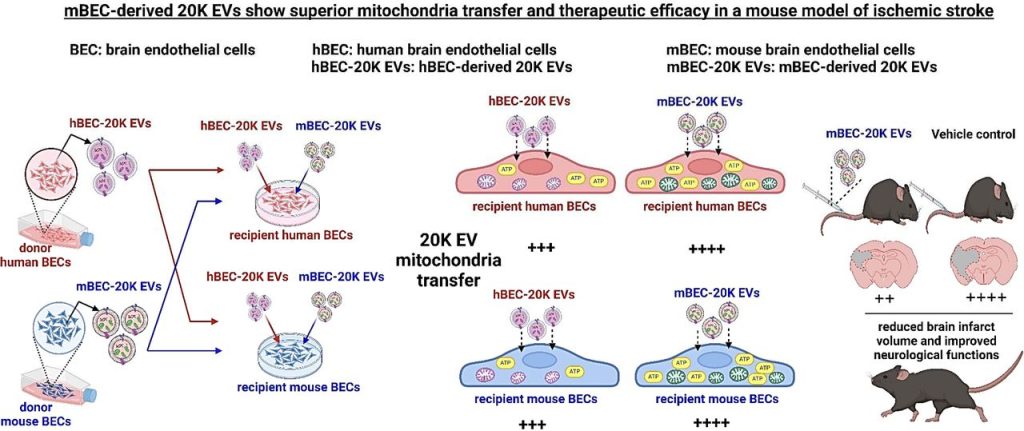
Building on this foundation, the team investigated whether EVs derived from donor species closely related to the recipient species could enhance therapeutic efficacy. They specifically studied mouse BEC (mBEC)-derived EVs in improving post-stroke outcomes in MCAo mice.
Their research compared EVs derived from the same species as the recipient cells (mBEC-EVs for mBECs, hBEC-EVs for hBECs) versus cross-species EVs (mBEC-EVs for hBECs and vice versa). The findings indicated that mBEC-EVs showed superior efficacy compared to hBEC-EVs. Notably, mBEC-EVs significantly increased ATP levels and enhanced mitochondrial function in recipient mBECs by improving oxygen consumption rates.
Crucially, administration of mBEC-EVs led to substantial reductions in brain infarct volume and neurological deficits in MCAo mice compared to those treated with vehicle alone.
These findings underscore the promising role of EVs in delivering mitochondria to stroke-affected cells, suggesting potential advancements in stroke treatment. Stay updated as this research progresses towards clinical applications.
Photo credits: Dave, Kandarp M., et al. “Mitochondria-containing extracellular vesicles from mouse vs. human brain endothelial cells for ischemic stroke therapy.” bioRxiv (2024): 2024-01.